Springs In Series Equation . Stretch and compress springs to explore the. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. consider two springs placed in series with a mass on the bottom of the second. The force is the same on each of the two springs. series and parallel springs. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. Therefore each spring extends the same amount. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. i the springs are identical:
from www.chegg.com
K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. i the springs are identical: Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. series and parallel springs. consider two springs placed in series with a mass on the bottom of the second. Stretch and compress springs to explore the. Therefore each spring extends the same amount. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel.
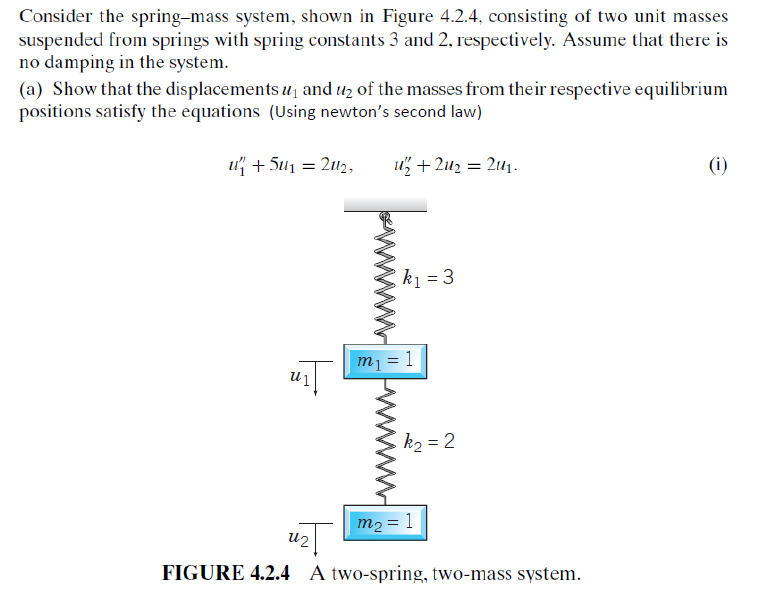
Consider the springmass system, shown in Figure
Springs In Series Equation K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. The force is the same on each of the two springs. series and parallel springs. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. Therefore each spring extends the same amount. i the springs are identical: Stretch and compress springs to explore the. consider two springs placed in series with a mass on the bottom of the second. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations.
From study.com
Spring Constant Formula, Law & Examples Video & Lesson Transcript Springs In Series Equation The force is the same on each of the two springs. Stretch and compress springs to explore the. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. consider two springs placed in series with a mass on the bottom of the second. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for. Springs In Series Equation.
From exoberrak.blob.core.windows.net
Equation For Springs In Series at Brian Hartley blog Springs In Series Equation K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k.. Springs In Series Equation.
From isaacphysics.org
Isaac Physics Springs In Series Equation K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. i the springs are identical: Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. understand key principles and master the. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Mass on spring equation of motion YouTube Springs In Series Equation Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. understand key principles and master the calculation of. Springs In Series Equation.
From exoberrak.blob.core.windows.net
Equation For Springs In Series at Brian Hartley blog Springs In Series Equation Therefore each spring extends the same amount. Stretch and compress springs to explore the. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Consider the springmass system, shown in Figure Springs In Series Equation Therefore each spring extends the same amount. consider two springs placed in series with a mass on the bottom of the second. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. series and parallel springs.. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Simple Harmonic Motion Springs in series vs parallel, and vertical Springs In Series Equation understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Springs in Series Verse Parallel Find Spring Constant YouTube Springs In Series Equation investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. Stretch and compress springs to explore the. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. consider two springs placed in series with. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.toppr.com
A mass m is suspended from the two coupled springs connected in series Springs In Series Equation understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. Stretch and compress springs to explore the. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. The force is the same on each of the two springs. Each. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.youtube.com
A Level Physics Springs in series and parallel YouTube Springs In Series Equation Stretch and compress springs to explore the. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. series and parallel springs. Each spring experiences the same pull from. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Spring constants in series and parallel YouTube Springs In Series Equation K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. series and parallel springs. i the springs are identical: Therefore each spring extends the same amount. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. The force is the same on each of the. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Any combination of springs connected in series Springs In Series Equation series and parallel springs. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. Therefore each spring extends the same amount. K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2). Springs In Series Equation.
From www.youtube.com
How to Derive Springs in Series Quickly A Level Physics YouTube Springs In Series Equation Stretch and compress springs to explore the. i the springs are identical: series and parallel springs. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. The force is the same on each of the two springs. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved 4. (5 pts) Demonstrate that the equivalent stiffness Springs In Series Equation Stretch and compress springs to explore the. Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. The force is the same on each of the two springs. i the springs are identical: investigate what. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.savemyexams.com
Hooke's Law CIE A Level Physics Revision Notes 2022 Springs In Series Equation The force is the same on each of the two springs. Using the spring rate (k) of each spring, an equivalent spring rate (k eq) can be determined depending on whether the springs are in. Therefore each spring extends the same amount. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. series and parallel springs. understand key principles. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.youtube.com
6.2b Ex1 FM19 P12 Q20 Springs Extension in Series AS Deformation Springs In Series Equation K eff = k 1 k 2 /(k 1 +k 2) = k/2. Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. Stretch and compress springs to explore the. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for. Springs In Series Equation.
From www.tes.com
How to Derive Springs in Series A Level Physics Teaching Resources Springs In Series Equation Therefore each spring extends the same amount. K eff = k 1+ k 2 = 2k. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. The force is the same on each of the two springs. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and parallel configurations. Using. Springs In Series Equation.
From studylib.net
parallel and series spring equations Springs In Series Equation Each spring experiences the same pull from the weight of the mass it supports. consider two springs placed in series with a mass on the bottom of the second. investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. understand key principles and master the calculation of the equivalent stiffness for springs in series and. Springs In Series Equation.